A new algorithm to predict the dynamic language of proteins
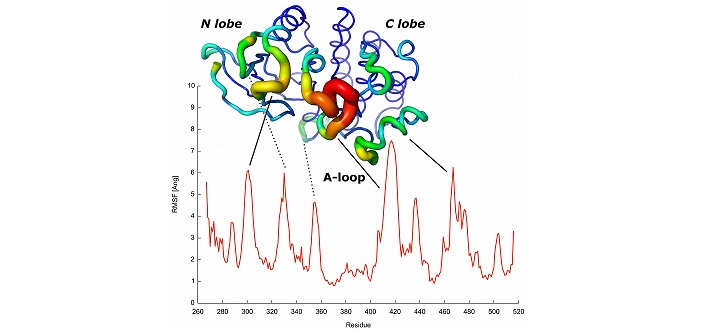
The predicted profile for the conformational dynamics of the tyrosine kinase family is shown. Regions highlighted in red correspond to important structural elements involved in protein activation.
Researchers from the Structural Biology Computational Group of the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), led by Alfonso Valencia, in collaboration with a group headed by Francesco Gervasio at the University College London (UK), have developed the first computational method based on evolutionary principles to predict protein dynamics, which explains the changes in the shape or dimensional structure that they experience in order to interact with other compounds or speed up chemical reactions. The study constitutes a major step forward in the computational study of protein dynamics (i.e. their movement), which is crucial for the design of drugs and for the research on genetic diseases, such as cancer, resulting in higher levels of complexity than allowed by current methods. The results have been published this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Proteins are macromolecules that are key to the thousands of cellular functions that take place in a living organism. They are formed by chains of smaller molecules called amino acids that fold forming a three-dimensional structure. It has recently been discovered that by studying the co-evolution of amino acids we can reconstruct the form or structure of these biological compounds in their natural surroundings. "A protein's amino acids can co-evolve, i.e. change in a coordinated way," says Alfonso Valencia. "By analysing the sequences of a given family of proteins, we can predict physical contacts between amino acids with great precision, in sufficient number to reconstruct the folding of a protein accurately and, therefore, its structure or form."
However, this structure does not remain static; it goes through changes in such a way that, similar to a dance in which each of the dancers adapts to their partner, it interacts with other biological compounds or with drugs. This is known as protein dynamics, the study of which has proven to be very difficult both with experimental observations and using computational tools.
The question addressed by the researchers at the beginning of the study, when Francesco Gervasio headed the Computational Biophysics Group at the CNIO, was more complex: can we use co-evolutionary studies to predict changes in the shape of proteins and, consequently, the language they establish with their environment?
"We developed a model in which the amino acids that have a strong co-evolutionary relationship attracted each other, without further additional data," says Simone Marsili, researcher who has also participated in the project. "First, we simulate the folding process and then we can see how the simulations were able to predict the changes in shape of the proteins at different levels of complexity, including those required for kinases to function [these are key proteins in metabolic and cell signalling processes as well as in cell transport, amongst others]."
This new computational method easily integrates experimental and genomic data through the use of the latest sequence analysis and 3D modelling technology. In addition, it demonstrates that genomic data can be a source of useful information to supplement the current tools used to study the structure and dynamics of proteins.
"The ability to predict key features of proteins at this level of complexity will help to understand how the sequence of a protein determines its dynamics and, therefore, its functions," concludes Valencia. This field of knowledge is key to the study of genetic diseases, such as cancer, or the design of drugs, amongst other uses.
Source: Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Oncologicas (CNIO)
BİOLOGY NEWS
-
RNA from Trained Aplysia Can Induce an Epigenetic Engram for Long-Term Sensitization in Untrained Aplysia.
-
HOW WE BECOME HAPPY
-
More tomatoes, faster: Accelerating tomato engineering
-
Purest yet liver-like cells generated from induced pluripotent stem cells
-
Legions of nanorobots target cancerous tumors with precision
-
CRISPR gene editing reveals new therapeutic approach for blood disorders
-
Quantum dots with impermeable shell: A powerful tool for nanoengineering
-
Thousands on one chip: New method to study proteins
-
Gene Drive Technology: Where is the future?
-
Four newly identified genes could improve rice
-
Watching the luminescent gene switch
-
DNA damage by ultrashort pulses of intense laser light
-
Mantis shrimp inspires next generation of ultra-strong materials
-
Specialized life forms abound at Arctic methane seeps
-
Ocean warming and acidification impact on calcareous phytoplankton